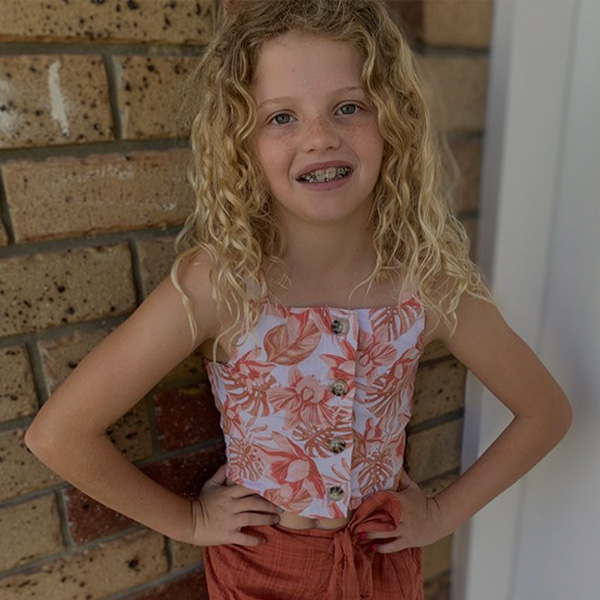
Prevent more serious problems from developing and reduce the complexity of treatment later in life.
The sooner problems can be identified and evaluated by your orthodontist, the sooner an appropriate treatment plan can be discussed with you. Your child’s treatment may not start right away but planning their care is equally as important. Dr Patty Medland is a specialist in paediatrics, holding qualifications in both orthodontics and children’s dentistry. This makes her the best person for the job when it comes to creating fantastic, long-lasting results.
Growth & Guidance
To help parents make informed decisions at the right times, Medland Orthodontics has introduced a Growth Guidance Program for children between 7-12 years. Rest easy that you will always be informed about the health of your child’s teeth and offered the best treatment plan for them.
Kids Orthodontics
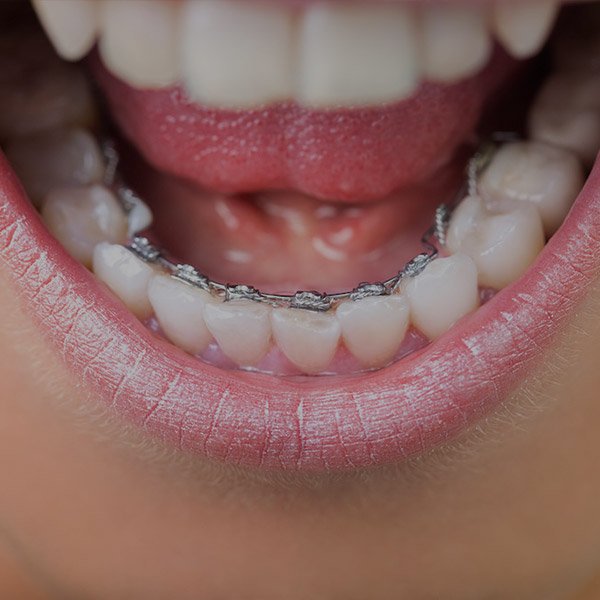
Kids braces can be a really great treatment for kids whose adult teeth are coming in and have started causing them issues. As the traditional and trusted orthodontic treatment, braces will have great results for your child.
A less-visible alternative to braces, Invisalign is a really popular option for kids orthodontics and can often help kids to feel more comfortable with their treatment. They’re also easy to clean and maintain for children of all ages.
For some kids, lingual braces are a great alternative to traditional braces as they sit on the inside of your child’s teeth. This means that they are far less noticeable yet equally effective.
Dental Issues Treated
The treatment process
Consultation
Impressions
Fitting
Adjustments
Debanding
(braces only)
Retainers
Frequently Asked Questions
When should my child see an orthodontist?
At what age do kids get braces?
Traditionally, treatment with invisalign/ braces begins when a child has lost most of his or her baby (primary) teeth, and a majority of the adult (permanent) teeth have grown in — usually between the ages of 8 and 14.
Does my kid really need braces?
Signs To Look For if Your Child Needs Braces
- Irregular, early, or late with losing baby teeth.
- Trouble/pain chewing or biting.
- Crowded or blocked teeth.
- A jaw that constantly shifts or make noises when moved.
- Teeth that don’t align or touch at all.
- Your child bites their cheeks a lot.